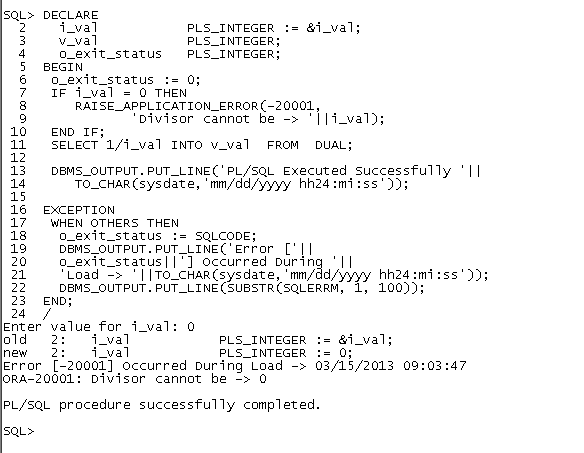
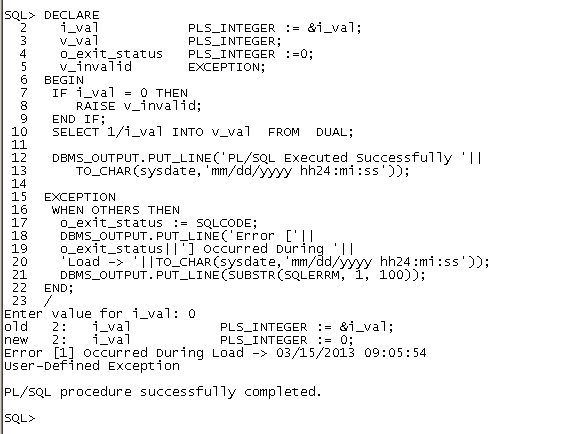
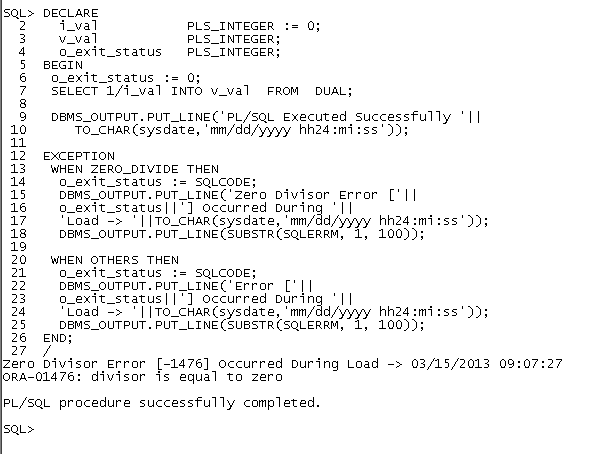
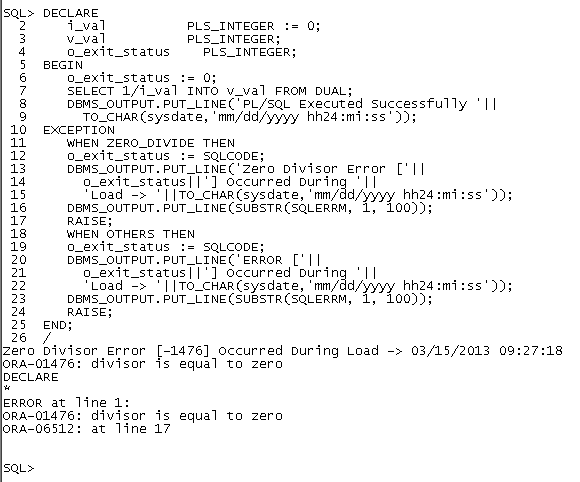
i_val PLS_INTEGER := &i_val;
v_val PLS_INTEGER;
o_exit_status PLS_INTEGER;
BEGIN
o_exit_status := 0;
IF i_val = 0 THEN
RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(-20001,
'Divisor cannot be -> '||i_val);
END IF;
SELECT 1/i_val INTO v_val FROM DUAL;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('PL/SQL Executed Successfully '||
TO_CHAR(sysdate,'mm/dd/yyyy hh24:mi:ss'));
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
o_exit_status := SQLCODE;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Error ['||
o_exit_status||'] Occurred During '||
'Load -> '||TO_CHAR(sysdate,'mm/dd/yyyy hh24:mi:ss'));
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(SUBSTR(SQLERRM, 1, 100));
END;
/